What is Inflammation & Why the Fuss?
Inflammation is a protective mechanism that allows your body to defend itself against infection, illness, or injury. It can also occur on a chronic basis, which can lead to various diseases.
 Put simply there are two types of inflammation.
Put simply there are two types of inflammation.
The first type is classical inflammation, which generates the inflammatory response we associate with injury or infection such as, heat, redness, swelling and pain.
The second type is chronic cellular inflammation, which is below the perception of pain. Chronic cellular inflammation is the initiating cause of many chronic diseases because it disrupts hormonal signalling networks throughout the body.
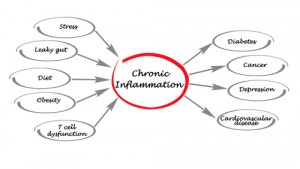
Why the Fuss? There is now ample evidence to suggest that chronic inflammatory changes are the root cause of many of the preventable chronic diseases that afflict modern industrial western society and is an emerging problem in many 3rd world countries.
How does chronic inflammation impact the body?
When you have chronic inflammation, your body’s inflammatory response can eventually start damaging healthy cells, tissues, and organs. Over time, this can lead to DNA damage, tissue death, and internal scarring.
All of these are linked to the development of several diseases, including:
- Cancer
- Cardio-Vascular Disease
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Obesity
- Metabolic Syndrome
- Asthma
- Some forms of cognitive decline& neuro-degenerative diseases such as dementia & Alzheimer’s disease
What Causes Chronic Inflammation?
- Certain lifestyle factors — especially habitual ones — such as the regular consumption of fast food, snacking when not hungry and smoking contribute to chronic inflammation
- Elevated levels of cortisol in response to chronically high stress levels is also known to contribute to the inflammatory process
- Consuming high amounts of sugar and high-fructose corn syrup is particularly harmful. It can lead to insulin resistance, diabetes, and obesity. Remember that many packaged & highly processed foods contain hidden sugar – think biscuits, breakfast cereal & juices, not to mention sugar that we might add to our tea or coffee.
- Scientists have also hypothesised that consuming a lot of refined carbs, such as white bread, may contribute to inflammation, insulin resistance, and obesity
- What’s more, eating processed and packaged foods that contain trans fats has been shown to promote inflammation and damage the endothelial cells that line your arteries
- Vegetable oils used in many processed foods are another possible culprit as are hydrogenated fats such as margarine. Regular consumption may result in an imbalance of omega-6 to omega-3 fatty acids, which some scientists believe may promote inflammation
- Excessive intake of alcohol and processed meat can also have inflammatory effects on your body
- Additionally, an inactive lifestyle that includes a lot of sitting is a major non-dietary factor that can promote inflammation
The Role of Diet in Inflammation
If you want to reduce inflammation, eat fewer inflammatory foods and more anti-inflammatory foods.
 Base your diet on whole, nutrient-dense foods that contain antioxidants — and avoid processed products.
Base your diet on whole, nutrient-dense foods that contain antioxidants — and avoid processed products.
Antioxidants work by reducing levels of free radicals. These reactive molecules are created as a natural part of your metabolism but can lead to inflammation when they’re not held in check.
Your anti-inflammatory diet should provide a healthy balance of protein, carbs, and healthy fat at each meal. Make sure you also meet your body’s needs for vitamins, minerals, fibre, and water.
One diet considered anti-inflammatory is the Mediterranean diet, which has been shown to reduce inflammatory markers, such as CRP and IL-6
A low-carb diet also reduces inflammation, particularly for people who are obese or have metabolic syndrome
In addition, vegetarian diets are linked to reduced inflammation .
Foods to Avoid
Some foods are associated with an increased risk of chronic inflammation.
 Consider minimising or cutting these out completely
Consider minimising or cutting these out completely
- Sugary beverages: Sugar-sweetened drinks and fruit juices
- Desserts: Biscuits, lollies, cake, and ice cream
- Processed meats: Hot dogs, salamis, sausages etc.
- Refined carbs: White bread, white pasta, etc.
- Processed snack foods: Crackers, chips, and pretzels
- Fried Foods: hot chips, battered fish etc
- Certain oils: Processed seed and vegetable oils like soybean and corn oil
- Trans fats: Foods with partially hydrogenated ingredients
- Alcohol: Excessive alcohol consumption
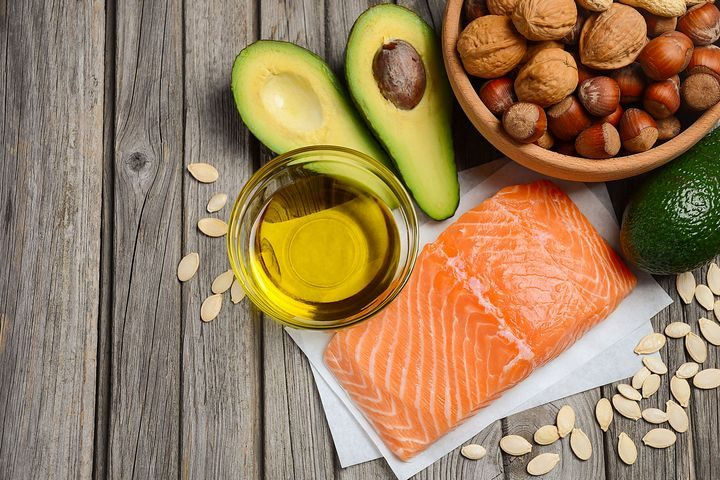
 Foods to Eat
Foods to Eat
Include plenty of these anti-inflammatory foods:
- Vegetables:Broccoli, kale, Brussels sprouts, cabbage, cauliflower, etc.
- Fruit:Especially deeply coloured berries like grapes and cherries
- High-fat fruits:Avocados and olives
- Healthy fats:Olive oil
- Fatty fish:Salmon, sardines, herring, mackerel, and anchovies
- Nuts: Almonds and other nuts
Plan Your Meals
It’s easier to stick to a diet when you have a plan. Dr. Sandi & the team at Como Diagnostic work together with  you to design a plan for your specific needs – remember even the best anti-inflammatory eating plan needs to take into account your current weight and energy expenditure. Excess energy intake will still convert to excess kilograms on the scale!
you to design a plan for your specific needs – remember even the best anti-inflammatory eating plan needs to take into account your current weight and energy expenditure. Excess energy intake will still convert to excess kilograms on the scale!
Other Helpful Tips
Once you have your healthy menu organized, make sure you incorporate these other good habits of an anti-inflammatory lifestyle:
- Supplements:Certain supplements can help reduce inflammation such as omega 3 fish oil
- Regular exercise:Exercise can decrease inflammatory markers and your risk of chronic disease
- Sleep:Getting enough sleep is extremely important. Researchers have found that a poor night’s sleep increases inflammation
The Pay Off of an Improved Lifestyle
An anti-inflammatory diet, along with exercise and good sleep, provides many benefits:
- Improvement of symptoms of arthritis, and some autoimmune disorders
- Decreased risk of obesity, heart disease, diabetes, depression, cancer, and other diseases
- Reduction in inflammatory markers in your blood
- Better blood sugar, cholesterol, and triglyceride levels
- Reduced cravings and high satiety makes it ideal for weight loss and weight management
- Improvement in energy and mood
- Following an anti-inflammatory diet and lifestyle may improve markers of inflammation and reduce your risk of many diseases.
The Bottom Line
Chronic inflammation is unhealthy and recent evidence suggests that it forms the basis of many of the preventable chronic diseases so prevalent in the west. A clear link between diet and lifestyle as the drivers of inflammation is now evident.
Choosing anti-inflammatory foods for optimal health and well-being along with other key lifestyle changes can markedly lower your risk of disease and improve your quality of life – it’s never too late to start!
Would you like to know more about your risk factors for chronic inflammation, learn simple and easy ways to eat healthily along with other lifestyle changes that can really make a difference to your feeling of well being? Dr. Sandi and our team of medical nutritionists are passionate advocates of anti- inflammatory nutrition and our programs for weight loss, weight management or just better nutrition in & of itself accords with these principles.
Your individually tailored anti- inflammatory nutrition program is just a phone call or an email way!
Ring us on 03 9826 4300 or email us at reception@comodiagnostic.com.au, we’d be delighted to be of assistance.